Request–Response
The request–response enables clients to send a request to the server and receive a direct response.
Server-Side Example (Rust)
This example demonstrates handling request–response events, where the server responds to specific client requests. For example:
myip: Returns the client's IP address.uppercase: Converts the provided message to uppercase and sends it back.
use axum_socket_io::{Procedure, SocketIo};
use std::net::SocketAddr;
pub async fn handle_socket(mut socket: SocketIo, addr: SocketAddr) {
println!("A user connected: {addr:#?}");
while let Ok(ev) = socket.recv().await {
match ev {
/* ... */
Procedure::Notify(req) => match req.method() {
"ping" => socket.notify("pong", req.data()).await.unwrap(),
_ => {}
},
Procedure::Call(req, res, _) => match req.method() {
"myip" => res.send(addr.to_string()).await.unwrap(),
"uppercase" => {
let msg = std::str::from_utf8(req.data()).unwrap();
res.send(msg.to_uppercase()).await.unwrap()
}
_ => {}
},
}
}
println!("user disconnected: {addr:#?}");
}Client-Side Example (JavaScript)
<script type="module">
import { SocketIo } from "https://esm.sh/client-socket-io@0.1.0";
const decodeText = data => new TextDecoder().decode(data);
window.socket = new SocketIo("ws://127.0.0.1:3000/socket");
await socket.connect();
window.rpc = async (...args) => decodeText(await socket.call(...args))
async function onPong() {
for await (const msg of socket.on("pong")) {
console.log("[Pong]", decodeText(msg));
}
}
[onPong].forEach((fn) => fn().catch(console.error));
</script>
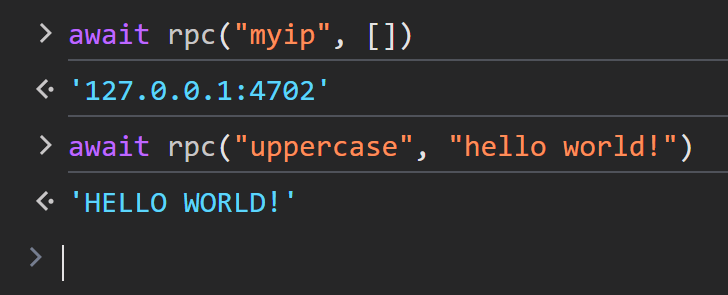
The socket.call(...) method is used to send a request to the server and wait for a response.